The extent of binding to proteins is an important parameter to assess when screening drug candidates during in-vitro ADME studies. Assessing the free fraction of drug available in the biological system is critical to understanding its distribution potential, as it is generally believed that the free fraction drives therapeutic outcomes since it is the free drug (that which is not bound to proteins) that can move to and interact with the sites of action, and high binding to proteins can affect the metabolism and elimination of the drug.
There are three methods most commonly used to assess protein binding, and it is important to assess their advantages and disadvantages when selecting methods to use for screening studies.
Rapid Equilibrium Dialysis (RED) makes use of a device with two chambers separated by a semipermeable membrane. Spiked matrix is added and over an incubation period, the free drug comes to equilibrium across the membrane while proteins and protein-bound drug cannot move across the membrane; free fraction is calculated by comparing the concentration of drug from the protein and protein-bound drug side to the protein-free, free drug side.
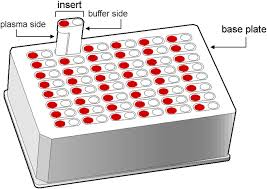
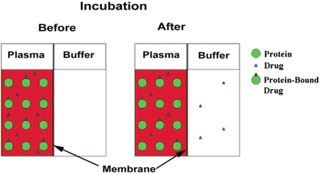
Advantages: Most common method (easy cross-comparisons), simple apparatus/setup and high throughput
Disadvantages: Requires long-term stability in the matrix (typical incubation period is 4 hours), nonspecific binding to the device/membrane, volume shifts and protein leakage over the incubation period.
Ultracentrifugation (UC) uses high-speed centrifugation to precipitate proteins and protein-bound drug from a spiked matrix; free fraction is calculated by comparing the concentration of drug in the protein-free supernatant and the intact spiked matrix.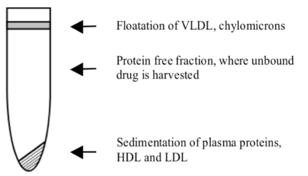 Advantages: Avoids membrane-related issues (nonspecific binding, leakage across membrane, etc.)
Advantages: Avoids membrane-related issues (nonspecific binding, leakage across membrane, etc.)
Disadvantages: Usually low-throughput, harder to control pH, temperature (conditions that can significantly affect protein binding), requires longer-term stability in matrix (typical centrifugation time is two hours), the supernatant may not be completely protein-free, leading to an artificially high free fraction observed.
Ultrafiltration (UF) uses a two-chambered device separated by a semipermeable filter. Spiked matrix is loaded into the device and centrifuged at moderate speed, during which time free drug passes through the filter while proteins and protein-bound drug cannot; free fraction is calculated by comparing the concentration of drug in the protein-free filtrate and the intact spiked matrix.
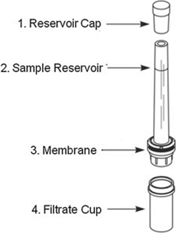 Advantages: Suitable for unstable compounds (typical centrifugation time is 30 minutes), quick and technically simple, high throughput/useful to screen many compounds to rank free fraction
Advantages: Suitable for unstable compounds (typical centrifugation time is 30 minutes), quick and technically simple, high throughput/useful to screen many compounds to rank free fraction
Disadvantages: Nonspecific binding to the filter membrane or collection chamber (under-estimation of free fraction), molecular sieving may occur (liquid moves through filter more quickly than the drug, under-estimating free fraction)




.jpg?width=2258&name=IMG_5349%20(002).jpg)
 Alliance Pharma has hired Dr. Ryan Klein as Director of Business Development. Dr. Klein has more than 20 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry developing both oral and topical dosage forms for a range of indications. Dr. Klein began his career at GlaxoSmithKline, where he was an integral component of their drug discovery organization providing drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic expertise to project teams. He was instrumental in the development and implementation of a number of in vitro and in situ ADME models to assess drug absorption, metabolism, and disposition.
Alliance Pharma has hired Dr. Ryan Klein as Director of Business Development. Dr. Klein has more than 20 years of experience in the pharmaceutical industry developing both oral and topical dosage forms for a range of indications. Dr. Klein began his career at GlaxoSmithKline, where he was an integral component of their drug discovery organization providing drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic expertise to project teams. He was instrumental in the development and implementation of a number of in vitro and in situ ADME models to assess drug absorption, metabolism, and disposition.